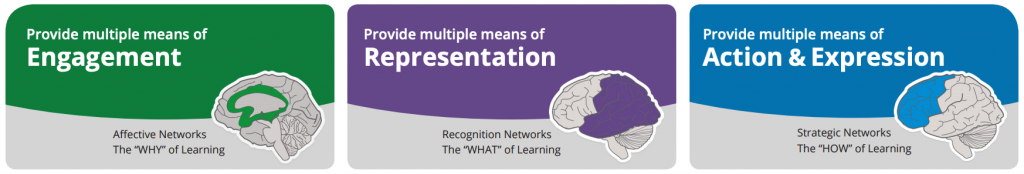
What is UDL?
The universal design for learning (UDL) framework provides an approach to designing environments that support learning variability. UDL practices help ensure all learners can meet learning goals by removing barriers to learning, and building flexibility into the curriculum. It provides a blueprint for designing strategies, materials, and assessments, to reach and teach all students, including those with diverse needs. Most practices are tweaks to course design that make learning more accessible for all students.